Rhinitis Introduction
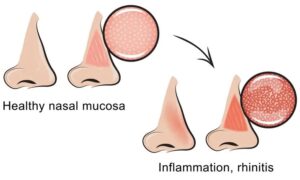 Rhinitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the nose. It is commonly referred to as “nasal inflammation” or simply “a runny nose.” Rhinitis can be caused by various factors, including allergies, infections, irritants, and hormonal changes.
The two main types of rhinitis are allergic rhinitis and non-allergic rhinitis. Allergic rhinitis occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods, leading to nasal inflammation and symptoms like sneezing, itching, a runny or congested nose, and watery eyes. Non-allergic rhinitis, on the other hand, is not triggered by allergens but may be caused by irritants like smoke, strong odors, changes in weather, or certain medications. It can also be associated with hormonal imbalances or structural abnormalities in the nose.
Rhinitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane lining the nose. It is commonly referred to as “nasal inflammation” or simply “a runny nose.” Rhinitis can be caused by various factors, including allergies, infections, irritants, and hormonal changes.
The two main types of rhinitis are allergic rhinitis and non-allergic rhinitis. Allergic rhinitis occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain foods, leading to nasal inflammation and symptoms like sneezing, itching, a runny or congested nose, and watery eyes. Non-allergic rhinitis, on the other hand, is not triggered by allergens but may be caused by irritants like smoke, strong odors, changes in weather, or certain medications. It can also be associated with hormonal imbalances or structural abnormalities in the nose. Causes
1. Allergens:
Allergic rhinitis is commonly triggered by allergens such as pollen, mold spores, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods. When a person with allergies comes into contact with these allergens, their immune system reacts by releasing chemicals like histamine, which leads to inflammation and symptoms of rhinitis.
2. Irritants:
Non-allergic rhinitis can be caused by irritants such as smoke, strong odors, air pollution, chemical fumes, cleaning products, and certain medications (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). These irritants can directly irritate the nasal passages and trigger inflammation.
3. Infections:
Viral or bacterial infections, such as the common cold or sinusitis, can cause rhinitis symptoms. Infections lead to inflammation and increased production of mucus in the nasal passages.
4. Hormonal changes:
Some individuals may experience rhinitis symptoms due to hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy or hormonal fluctuations associated with the menstrual cycle. These changes can affect the nasal blood vessels and increase nasal congestion.
5. Structural abnormalities:
Certain structural abnormalities in the nose, such as a deviated septum (a crooked partition between the nostrils) or nasal polyps (abnormal growths in the nasal cavity), can obstruct airflow and contribute to chronic rhinitis symptoms.
6. Occupational factors:
Occupational rhinitis is caused by exposure to certain substances in the workplace, such as dust, chemicals, or allergens specific to certain industries (e.g., woodworkers, hairdressers, bakers).
Allergic rhinitis is commonly triggered by allergens such as pollen, mold spores, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods. When a person with allergies comes into contact with these allergens, their immune system reacts by releasing chemicals like histamine, which leads to inflammation and symptoms of rhinitis.
2. Irritants:
Non-allergic rhinitis can be caused by irritants such as smoke, strong odors, air pollution, chemical fumes, cleaning products, and certain medications (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). These irritants can directly irritate the nasal passages and trigger inflammation.
3. Infections:
Viral or bacterial infections, such as the common cold or sinusitis, can cause rhinitis symptoms. Infections lead to inflammation and increased production of mucus in the nasal passages.
4. Hormonal changes:
Some individuals may experience rhinitis symptoms due to hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy or hormonal fluctuations associated with the menstrual cycle. These changes can affect the nasal blood vessels and increase nasal congestion.
5. Structural abnormalities:
Certain structural abnormalities in the nose, such as a deviated septum (a crooked partition between the nostrils) or nasal polyps (abnormal growths in the nasal cavity), can obstruct airflow and contribute to chronic rhinitis symptoms.
6. Occupational factors:
Occupational rhinitis is caused by exposure to certain substances in the workplace, such as dust, chemicals, or allergens specific to certain industries (e.g., woodworkers, hairdressers, bakers).
Symptoms
1. Nasal congestion:
A feeling of stuffiness or blockage in the nose due to swollen nasal tissues and increased mucus production.
2. Runny nose:
Excessive nasal discharge, which can be clear and watery (in allergic rhinitis) or thick and colored (in non-allergic rhinitis or infections).
3. Sneezing:
Frequent or repetitive sneezing, often in response to irritants or allergens.
4. Itching:
Itching sensation in the nose, throat, or eyes, particularly in allergic rhinitis. It may be accompanied by redness and watery eyes.
5. Post-nasal drip:
Mucus dripping down the back of the throat, leading to a sensation of needing to clear the throat frequently or coughing.
6. Reduced sense of smell:
Nasal inflammation can affect the sense of smell, leading to a decreased ability to detect odors. <
strong>7. Facial pressure or pain:
In some cases, rhinitis can cause discomfort or pain in the face, particularly around the sinuses.
A feeling of stuffiness or blockage in the nose due to swollen nasal tissues and increased mucus production.
2. Runny nose:
Excessive nasal discharge, which can be clear and watery (in allergic rhinitis) or thick and colored (in non-allergic rhinitis or infections).
3. Sneezing:
Frequent or repetitive sneezing, often in response to irritants or allergens.
4. Itching:
Itching sensation in the nose, throat, or eyes, particularly in allergic rhinitis. It may be accompanied by redness and watery eyes.
5. Post-nasal drip:
Mucus dripping down the back of the throat, leading to a sensation of needing to clear the throat frequently or coughing.
6. Reduced sense of smell:
Nasal inflammation can affect the sense of smell, leading to a decreased ability to detect odors. <
strong>7. Facial pressure or pain:
In some cases, rhinitis can cause discomfort or pain in the face, particularly around the sinuses.
Preventions
1. Allergen avoidance:
If you have allergic rhinitis, identifying and avoiding allergens that trigger your symptoms can be helpful. For example, if you are allergic to pollen, you can stay indoors when pollen counts are high, keep windows closed, use air purifiers, and avoid spending time in grassy areas.
2. Dust mite reduction:
If dust mites are a trigger for your rhinitis, take steps to reduce their presence in your environment. This may include using dust mite-proof covers for bedding, washing bedding regularly in hot water, and minimizing carpeting and stuffed animals in your home.
3. Pet care:
If you are allergic to pet dander, try to limit exposure to pets, particularly those with fur or feathers. Avoid allowing them in your bedroom, and wash your hands thoroughly after touching pets.
4. Indoor air quality:
Keep indoor environments well-ventilated and free from smoke, strong odors, and other irritants. Consider using air purifiers or filters to help reduce allergens and pollutants in the air.
5. Hygiene practices:
Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently, especially during cold and flu seasons, to reduce the risk of viral infections that can lead to rhinitis symptoms.
6. Nasal irrigation:
Regularly rinsing your nasal passages with a saline solution (using a neti pot or nasal spray) can help clear irritants and reduce inflammation.
7. Stress management:
Stress can exacerbate rhinitis symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies to help manage stress levels.
If you have allergic rhinitis, identifying and avoiding allergens that trigger your symptoms can be helpful. For example, if you are allergic to pollen, you can stay indoors when pollen counts are high, keep windows closed, use air purifiers, and avoid spending time in grassy areas.
2. Dust mite reduction:
If dust mites are a trigger for your rhinitis, take steps to reduce their presence in your environment. This may include using dust mite-proof covers for bedding, washing bedding regularly in hot water, and minimizing carpeting and stuffed animals in your home.
3. Pet care:
If you are allergic to pet dander, try to limit exposure to pets, particularly those with fur or feathers. Avoid allowing them in your bedroom, and wash your hands thoroughly after touching pets.
4. Indoor air quality:
Keep indoor environments well-ventilated and free from smoke, strong odors, and other irritants. Consider using air purifiers or filters to help reduce allergens and pollutants in the air.
5. Hygiene practices:
Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently, especially during cold and flu seasons, to reduce the risk of viral infections that can lead to rhinitis symptoms.
6. Nasal irrigation:
Regularly rinsing your nasal passages with a saline solution (using a neti pot or nasal spray) can help clear irritants and reduce inflammation.
7. Stress management:
Stress can exacerbate rhinitis symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies to help manage stress levels.

